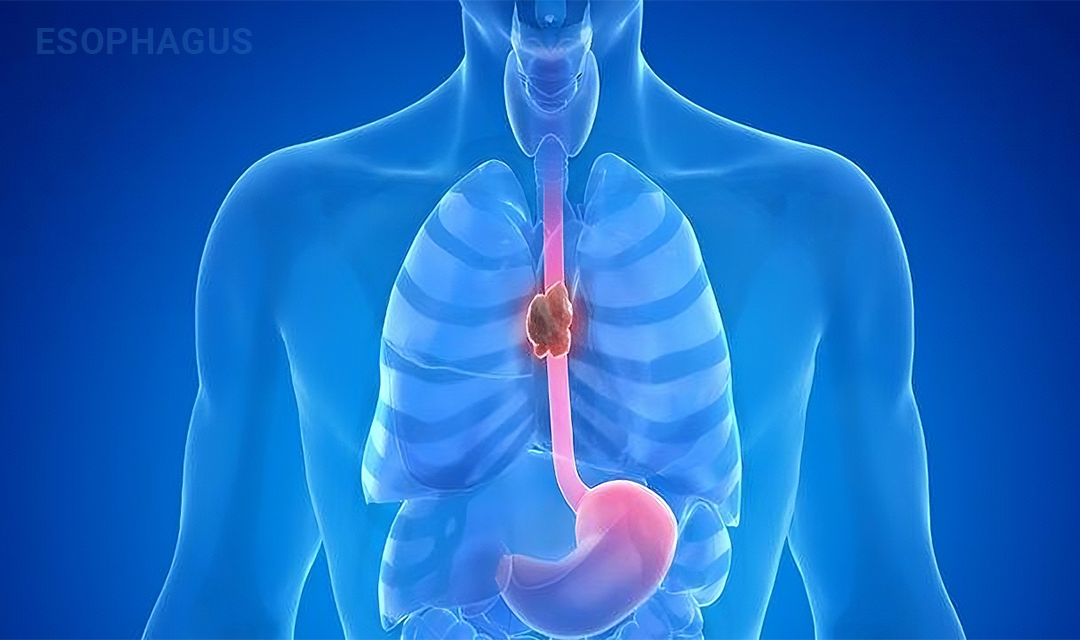
Understanding the Esophagus: Functions, Problems, and Solutions
What is the Esophagus?
The esophagus is a vital part of your digestive system, serving as the muscular tube that connects your throat (pharynx) to your stomach. Its main job is to transport food and liquids from your mouth to your stomach for digestion. However, when the esophagus encounters issues, it can lead to discomfort, swallowing difficulties, or more serious conditions that require medical attention.
How the Esophagus Works
- Swallowing: When you swallow, muscles in your throat and esophagus contract in a coordinated way to push food and liquids downward.
- Peristalsis: The esophagus performs rhythmic muscle contractions called peristalsis, which ensures food moves efficiently, even when you’re lying down.
- Lower Esophageal Sphincter (LES): This valve-like muscle at the junction of the esophagus and stomach opens to let food enter the stomach and closes to prevent stomach contents from refluxing back into the esophagus.
Common Symptoms of Esophageal Problems
- Heartburn: A burning sensation in the chest or throat, often caused by acid reflux.
- Dysphagia: Difficulty swallowing or the feeling of food being stuck in the throat or chest.
- Regurgitation: The sensation of stomach contents coming back up into the throat or mouth.
- Chest Pain: It may range from sharp to dull and can sometimes mimic heart-related discomfort.
- Chronic Cough: Especially common at night or after meals.
- Hoarseness: Changes in voice, often due to acid irritation of the throat.
Causes of Esophageal Problems
- Acid Reflux (GERD): Frequent backflow of stomach acid into the esophagus, leading to irritation.
- Esophagitis: Inflammation of the esophagus caused by acid reflux, infections, or certain medications.
- Esophageal Stricture: Narrowing of the esophagus due to scar tissue or chronic inflammation.
- Hiatal Hernia: When part of the stomach pushes through the diaphragm into the chest cavity.
- Esophageal Cancer: Tumors in the esophagus that can obstruct or bleed.
- Achalasia:A disorder in which the LES fails to relax properly, preventing food from entering the stomach.
“Dr. Varun's expertise in treating esophageal issues has been life-changing. Highly recommended for anyone dealing with severe GERD or esophageal cancer.”
Home Remedies for Esophageal Problems
For mild esophageal discomfort, these home remedies may help:
-
Managing Acid Reflux and Heartburn
- Elevate Your Head While Sleeping: Use a wedge pillow or raise the head of your bed to reduce acid reflux at night.
- Avoid Trigger Foods: Steer clear of spicy, fatty, or acidic foods, as well as caffeine, alcohol, and chocolate.
- Eat Smaller Meals: Large meals can increase stomach pressure and worsen reflux.
- Don’t Lie Down After Eating: Wait 2–3 hours after meals before lying down to help with digestion.
-
Soothing Irritation
- Ginger Tea: Ginger has anti-inflammatory properties that can ease irritation.
- Honey: A teaspoon of honey can coat the esophagus and provide temporary relief.
- Aloe Vera Juice: Drinking small amounts of pure aloe vera juice may reduce inflammation.
-
Improving Swallowing
- Chew Food Thoroughly: Make swallowing easier by breaking down food well.
- Stay Upright While Eating: Proper posture can help food pass through the esophagus smoothly.
Treatment Options for Esophageal Conditions
-
Lifestyle Changes:
- Eat smaller meals.
- Avoid foods that trigger symptoms.
- Maintain a healthy weight to reduce pressure on the stomach.
-
Medications:
- Antacids: Neutralize stomach acid.
- Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs) & H2 Blockers: Reduce acid production.
- Prokinetics: Help the esophagus move food more effectively.
-
Surgery:
- Fundoplication: Strengthens the LES to prevent acid reflux.
- Hiatal Hernia Repair: Repairs the stomach’s position to alleviate symptoms.
- Esophageal Dilation or Myotomy: For narrowing of the esophagus or achalasia.
- Esophageal Cancer Surgery: Removes tumors or damaged portions of the esophagus.
-
Endoscopic Procedures:
- Minimally invasive treatments for strictures or early-stage cancer.
-
Dietary Adjustments:
- Tailor your diet to avoid irritants and support healing.
When Is Surgery Necessary?
Surgery may be needed for:
- Severe GERD: If lifestyle changes and medications don’t provide relief.
- Hiatal Hernias: That cause persistent discomfort or complications.
- Esophageal Strictures or Achalasia: To restore proper swallowing function.
- Esophageal Cancer: To remove tumors or affected parts of the esophagus.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A Patient’s Experience

“Dr. Varun's expertise in treating esophageal issues has been life-changing. Highly recommended for anyone dealing with severe GERD or esophageal cancer.”
- Ravi Kumar
- Happy Patient

“I had been struggling with severe GERD for years. Dr. Varun’s treatment has made a significant difference. The personalized approach and advanced techniques were exactly what I needed.”
- Sita Rani
- Grateful Patient
Conclusion
- The esophagus is a critical component of digestion, and maintaining its health is essential for overall well-being. Whether you’re managing mild symptoms with home remedies or seeking advanced treatment for serious conditions, understanding your options is key. If you experience persistent or severe symptoms, consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and care. Early intervention can improve outcomes and help you live a healthier, more comfortable life.