Appendix Surgery in Guntur - Leading Gastro Surgeon
What is the Appendix?
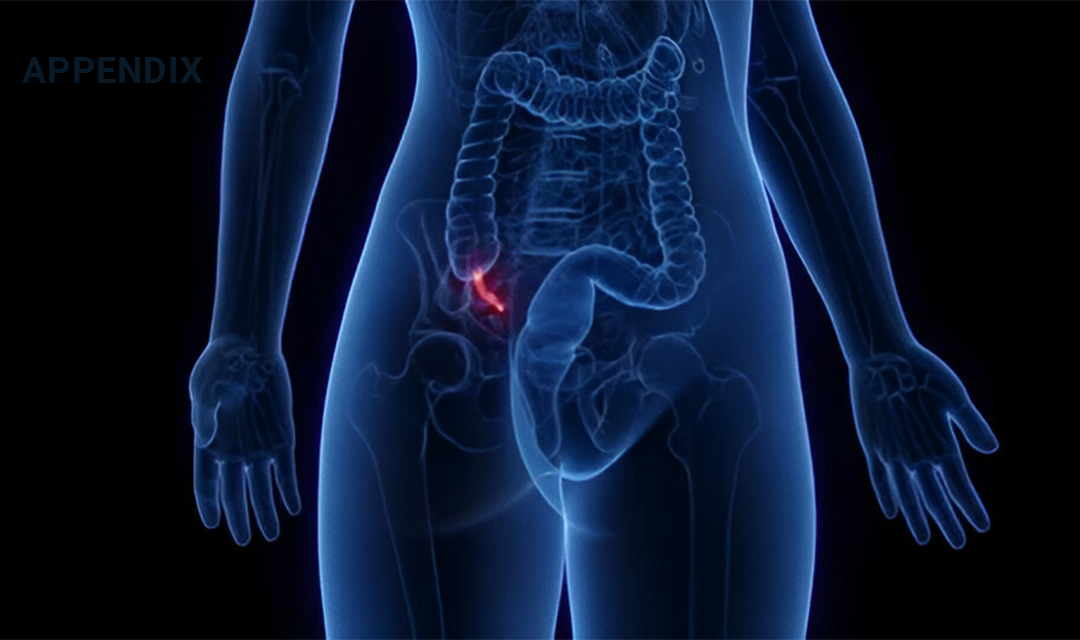
The appendix is a small, tube-shaped organ located in the lower right abdomen, connected to the large intestine. It is about 4 to 6 inches long and 0.5 inches in diameter. Its exact function is not entirely clear, but it may play a role in the immune system, particularly in early life.
How Does the Appendix Work?
- Immune Function:
- The appendix contains lymphoid tissue involved in the immune response and may help the body recognize and fight infections, especially during childhood.
- Gut Flora:
- It may help maintain a healthy balance of gut bacteria by acting as a reservoir for beneficial bacteria. These bacteria can repopulate the gut after gastrointestinal illness.
- No Essential Function:
- While the appendix has roles in immunity and gut flora, it is not essential for survival. Many people live healthy lives after appendix removal.
Symptoms of Appendix Problems
- Abdominal Pain: Pain often starts around the belly button and moves to the lower right abdomen. It may be sharp and worsen with movement or pressure.
- Nausea and Vomiting: Frequently accompanies abdominal pain.
- Loss of Appetite: Common in appendicitis.
- Fever: Mild to moderate fever may be present.
- Constipation or Diarrhea: Changes in bowel habits can occur with appendiceal inflammation.
- Swelling or Tenderness: In the lower right side of the abdomen.
Causes of Appendix Problems
- Appendicitis: Inflammation of the appendix, often caused by:
- Blockage: A blockage in the appendix, usually by stool, a foreign body, or cancer, can lead to inflammation and infection.
- Infection: Bacterial infections can cause appendicitis.
- Other Conditions: Such as inflammatory bowel disease or trauma.
- Appendiceal Abscess: A localized collection of pus around the appendix due to infection.
- Appendiceal Tumors: Rare tumors in the appendix, including:
- Carcinoid Tumors: Usually slow-growing and often found incidentally.
- Mucinous Cystadenomas: Tumors that can produce mucus.
- Appendiceal Hyperplasia: Benign enlargement of the appendix lining, often seen in conditions like Crohn’s disease.
“Dr. Varun offers expert care in appendix surgery, providing advanced solutions and relief for patients with appendix-related conditions in Guntur.”
Treatment Options
-
Medications:
- Antibiotics: Used to treat infections associated with appendicitis or appendiceal abscesses.
- Pain Relievers: To manage pain associated with appendicitis.
-
Surgical Intervention:
- Appendectomy: The surgical removal of the appendix, which is the standard treatment for appendicitis. It can be performed using:
- Open Surgery: A larger incision is made in the lower right abdomen.
- Laparoscopic Surgery: Minimally invasive surgery using small incisions and a camera.
- Appendectomy: The surgical removal of the appendix, which is the standard treatment for appendicitis. It can be performed using:
-
Supportive Care:
- Hydration and Nutrition: Managing symptoms and supporting recovery post-surgery.
- Antibiotics: Sometimes given pre-operatively to reduce infection risk.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A Patient’s Experience

“Dr. Varun’s expertise in appendix surgery has been life-changing. His advanced techniques and compassionate care have significantly improved my health.”
- Rajesh Kumar
- Satisfied Patient

“I am deeply grateful to Dr. Varun for his exceptional care in treating my appendix condition. His thorough approach and dedication have greatly enhanced my quality of life.”
- Anita Rao
- Thankful Patient